What LCD Modes Mean: Reflective, Transmissive, Transflective
Estimated reading time: 4 minutes
“Reflective”, “transmissive” and “transflective” are terms often used in connection with liquid crystal display (LCD) technology. They describe the ways in which LCD display modules are illuminated. In contrast to the emissive display technologies, like OLED displays (organic light-emitting diode) and VFDs (vacuum fluorescence displays), LCDs require a light source such as the sun, or artificial room light, or an integrated backlight, which is typically lit by LED (light-emitting diode) semiconductors.
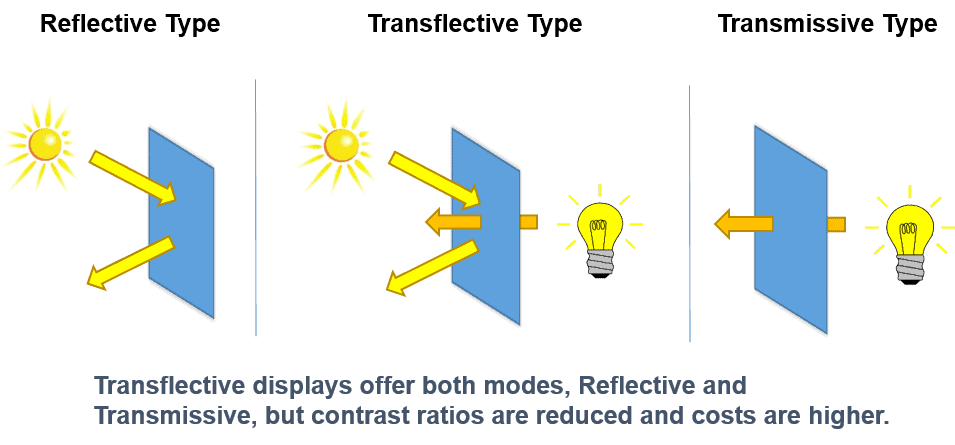
Transmissive LCD Mode
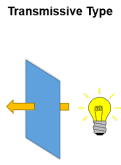
The mode of operation when light from a backlight passes through the LCD glass is called transmissive. The LCD glass or LCD panel functions as an “optical switch” where light from the backlight passes through the LCD cell depending on the orientation of liquid crystal molecules. The orientation can be “switched” on or off by an electrical field. Backlights produce a lot of light, making the display content very bright. The negative side of using backlights is that they require a significant amount of energy within an LCD display module, especially because the backlight is required to be on all the time even if there’s no content showing on the display. In direct sunlight, a transmissive LCD screen can become ‘washed-out’ if the sunlight overpowers the luminance of the backlight. Strong enough backlights to maintain sufficient contrast in direct sunlight – such as in aviation displays – are not compatible with the requirements of portable devices.
Reflective LCD Mode
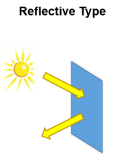
Some displays use ambient light rather than a backlight (View our Sun Vision Display brand of outdoor digital signage for an excellent example). This mode of operation is called reflective. In reflective mode, a mirror is installed behind the liquid crystal layer, either inside the LCD cell or on the rear polarizer. Ambient light passes through the LCD cell from the front side and is reflected by the mirror back to the viewer. The advantage is lower power consumption and excellent visibility in direct sunlight, making such displays excellent solutions for outdoor daytime applications. To be visible at night or in dark settings, reflective LCDs require additional lighting.
Transflective LCD Mode
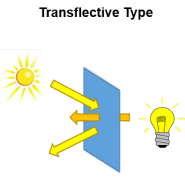
Transflective LCD displays have both transmissive and reflective characteristics. They contain an integrated backlight unit and a semi-transparent reflector or a reflector with a hole for each pixel. Again, the reflector can be behind the rear polarizer or inside the LCD cell behind the liquid crystal layer. Light from the backlight can pass the semi-transparent reflector and operate the display in the transmissive mode. At the same time, ambient light can be reflected so that the display is visible in direct sunlight as well. Care must be taken to account for the fact that in the transmissive mode of operation the light passes the liquid crystal layer once, while in the reflective mode it passes the liquid crystal layer twice. The appearance of transflective displays is a compromise. It is the most flexible solution as it allows for lower power consumption in bright environments and readability in any lighting condition. This comes at the expense of top performance in the pure illumination modes and sometimes significant additional manufacturing cost.
Summary
To summarize, LCD displays require an external light source. The way in which the light source is delivered to the LCD cell is the mode of operation and can either be reflective, transmissive, or transflective. For outdoor applications, a reflective or transflective LCD is preferred because of their energy efficiency. For indoor applications, a transmissive or transflective LCD is the best choice because they are viewable in dark lighting conditions.